1 问题及数据集
1.1 问题
本论文主要解决一种面向Cloze-style(填空式)的阅读理解(问答)问题
1.2 数据集
(1)CNN&Daily Mail
(2)SQuAD
(3)Graph Reachability datase
2 已有方法
2.1 单轮推理
(1)特点
单轮推理模型主要利用注意力机制来强调文档中与问题相关的那些部分,计算问题和文档子单元的相应加权表示之间的相关度,为候选目标评分。这好比在处理一些不太重要的部分的同时聚焦其他重要的部分,从而找到最后可能的答案。这种模型较简单,推理能力也不是很强。
(2) 方法
- Hermann et al. propose the attentive reader and the impatient reader models using neural networks with an attention over passages to predict candidates.
- Hill et al. use attention over window-based memory, which encodes a window of words around entity candidates, by leveraging an end- to-end memory network。
- Kadlec et al. propose the attention-sum reader to sum up all the attention scores for the same entity,This score captures the relevance between a query and a candidate. Chen
- Chen et al. propose using a bilinear term similarity function to calculate attention scores with pretrained word embeddings.
- Trischler et al. propose the EpiReader which uses two neural network structures: one extracts candidates using the attention-sum reader; the other reranks candidates based on a bilinear term similarity score calculated from query and passage representations。
2.2 多轮推理
(1)特点
对于复杂的段落以及复杂的问题,读者通常会再次阅读文档以获得更深层次的信息。多轮推理模型就是将问题和前面推理中获得的新信息结合,从而模拟这个重读过程,得到新的推理信息。不断的迭代推理,在若干推理后预测出答案。但现存的多轮推理模型通常都预定义了迭代的次数,而忽视了每一个问题或文档的复杂度。
(2)方法
- Hill et al. use multiple hops memory network to augment the query with new information from the previous hop。
- Gated Attention reader is an extension of the attention-sum reader with multiple iterations by pushing the query encoding into an attention-based gate in each iteration.
- Iterative Alternative (IA) reader produces a new query glimpse and document glimpse in each iteration and utilizes them alternatively in the next iteration.
- Cui et al. propose to extend the query-specific attention to both query-to-document attention and document-to-query attention, which is built from the intermediate results in the query-specific attention。
2.3 现有方法的问题
上面的两类模型,第一种模型可以看作是第二种模型的一种特例,其迭代次数为1,于是目前已有的方法都采用了固定推理的轮数。而人在面临阅读理解的时候,会根据问题和文章的难度动态的决定推理次数。
3 本文提出的方法
本文提出了ReasoNet模型,用于模拟人类阅读的过程,带着问题多次阅读原文,并设置一个终止状态,动态的决定推理的轮数,直到获得的信息足够用于回答问题时才停止推理过程。此外,又引入了强化学习算法CR(对比奖励)来训练模型。
4 具体内容
4.1 ReasoNet网络结构
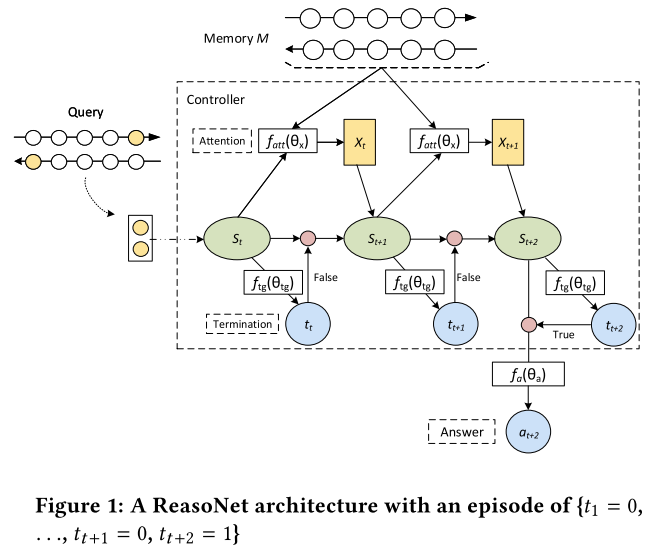
(1)Memory:外部记忆,Document Encoder产生的每个单词的上下文表示
(2)Attention:注意力向量(也叫上下文向量)xt是由当前状态和外部记忆进行计算得出的
(3)Internal State:内部状态S,初始状态s1是Query Encoder产生的问题表示,t时刻状态由RNN产生st=RNN(st−1,xt;θs);
(4)Termination Gate:根据当前内部状态产生一个binary随机变量。如果为1,那么结束推理预测答案;如果为0,那么继续推理
(5)Answer:当终止状态为1时,回答问题
4.2 具体步骤
(1)计算过程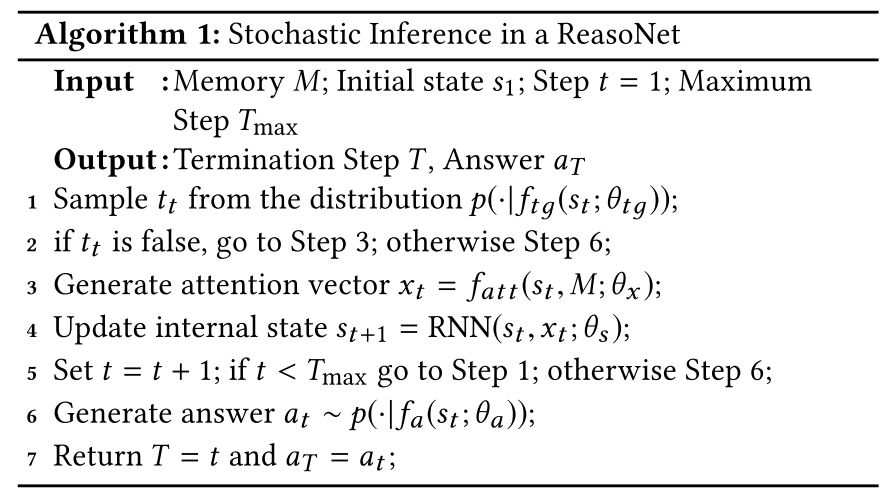
(2)需要学习的参数
- embedding matrices θW
- attention network θx
- the state RNN network θs
- the answer action network θa
- the termination gate network θtg Query
- Encoder和Document Encoder的参数(参考笔记中提出)
(3)期望奖励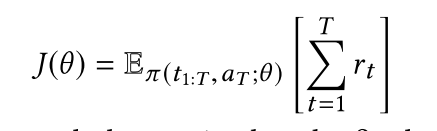
如果最终时刻的回答正确,则置Rt=1,否则为0,中间时刻的Rt=0。(具体细节还不是很清楚,先占坑,后面看了强化学习来填坑)
5 实验
5.1 CNN&Daily Mail Datasets
(1)实验配置
- vocab_size:|V| = 101k words in CNN,|V| = 151k words in Daily Mail
- Embedding Layer:300-dimensional word embeddings,300-dimensional pretrained Glove word embeddings,dropout with probability 0.2
- Bi-GRU Encoder:bidirectional GRU for encoding query and passage into vector representations,隐藏层单元个数:CNN256个,Daily Mail384个;用正交矩阵初始化GRU的权重;GRU的其他权重采用-0.01到+0.01之间的均匀随机分布。
- Memory and Attention:composed of query memory and pas- sage memory;
- Internal State Controller:choose GRU model as the internal state controller
- TerminationModule:adopt a logistical regression to model the termination variable at each time step
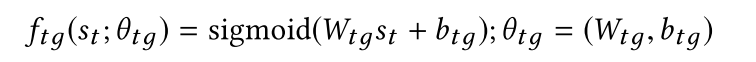
- 最大推理轮数为5
(2)实验结果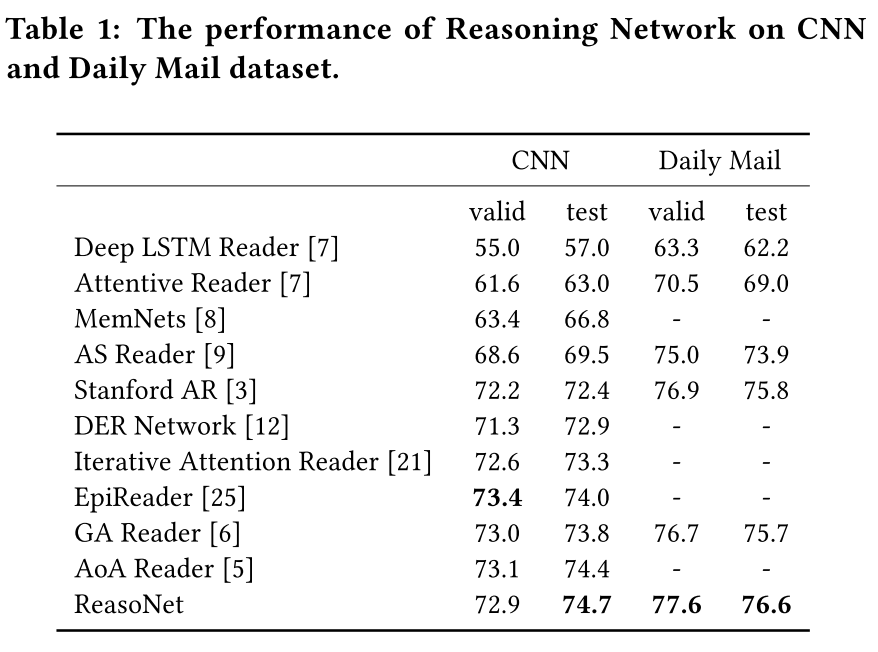
5.2 SQuAD
(1)实验配置
与前一个数据集的配置有一些区别,也是按照那几部分分别设置
(2)实验结果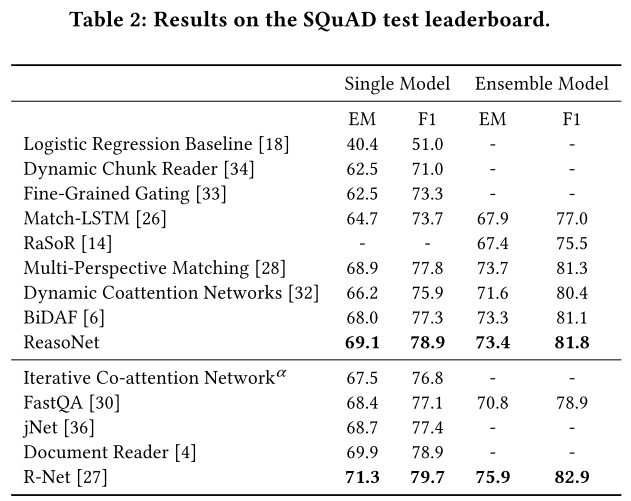
5.3 Graph Reachability Task
这种数据之前没了解过,先占坑,后面来填
6 笔记小结
(1)通过引入终止状态,使得模型能够动态的决定推理轮数
(2)通过强化学习来训练模型
(3)本篇论文只是读了个大概,很多细节都还没有具体去研究,不了解的点还非常多,先占坑,后面研究了强化学习再来把相应的坑补上。
资料来源
(1)论文地址
(2)相关论文笔记:学习如何停止阅读
(3)数据集CNN&Daily Mail
思维导图